Table of Contents
Polyethylene, commonly known as polythene, is a versatile synthetic polymer. It’s a widely used thermoplastic known for its flexibility, durability, and low cost. Polyethylene is classified into various types, including low-density (LDPE), high-density (HDPE), and linear low-density (LDPE). LDPE is used in plastic bags and packaging, while HDPE is found in items like milk jugs and water pipes. It combines the features of both. Its applications range from everyday items to medical devices. However, its non-biodegradable nature has prompted environmental concerns, driving efforts towards recycling and eco-friendly alternatives. Polyethylene’s adaptability continues to influence various industries and our daily lives.
What is polyethylene?
Polyethylene, often simply referred to as “polythene,” is a versatile and ubiquitous type of plastic. It’s produced from a substance called ethylene, and its widespread use is due to its remarkable combination of properties. One of its most notable features is its flexibility, which makes it suitable for various applications. Whether you’re carrying groceries in a plastic bag or drinking from a squeezable plastic bottle, you’re likely interacting with polyethylene products daily.
The toughness of polyethylene is another noteworthy characteristic. It can withstand the rigors of everyday life, making it a popular choice for products that need to endure wear and tear. Its durability also means it can be used for both single-use items, like disposable food containers, and for longer-lasting products, such as water pipes and outdoor furniture.
Affordability is another factor contributing to polyethylene’s popularity. It’s relatively inexpensive to manufacture, making it an attractive option for a wide range of consumer and industrial applications. The cost-effectiveness of polythene has led to its extensive use in various industries, from packaging to construction.
Despite its many advantages, polythene has a notable drawback: it doesn’t naturally decompose, making it non-biodegradable. This environmental concern has led to efforts to reduce its impact, primarily through recycling initiatives and the development of more environmentally friendly plastic alternatives.
In essence, polyethylene is a fundamental material in our modern world, providing convenience, durability, and cost-efficiency across a broad spectrum of products and industries. Its adaptability and wide-ranging applications continue to influence our daily lives, even as we work towards finding more sustainable solutions for the future.
Read More About Plastic Engineering
What is ethylene?
Ethylene is a substance that has many uses, and it can be made in different ways. One way is by mixing hydrogen with acetylene, which is a different chemical. Another method involves removing water from ethanol, which is a type of alcohol.
In some countries, they create ethylene from things like crude oil through a process known as cracking. It’s a bit like cooking, but with special equipment. They heat up substances like ethane or propane, which are also found in crude oil. By doing this, they can turn these substances into ethylene.
What’s interesting is that ethylene is usually a gas when it’s at normal room temperature, just like the air we breathe. But if you make it extremely cold, at around -104°C, it changes into a liquid. This property can be useful in certain industries and processes where extremely cold temperatures are needed for storage or specific reactions. So, ethylene’s ability to turn from a gas to a liquid can be pretty handy in various applications.
Types Of Polyethylene
There are two main types of polyethylene:
- Low density
- High density
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has molecules with little side branches, while high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is more like a straight chain.
To make it, they use a special process where they mix ethylene with oxygen under very high pressure, about 1500 times the pressure of the air we breathe, and heat it between 180 and 250°C. Surprisingly, just a tiny bit of oxygen (0.1%) can kickstart the whole thing. They can also use other chemicals like peroxides, hydroperoxides, and azo compounds to get it going.
LDPE gets soft and starts to melt at around 110–125 °C, but it’s not very organized; only about 40% of it is in a solid form. Its density is 0.91-0.92 grams per cubic centimeter. At regular room temperature, almost no liquid can dissolve it, but at higher temperatures, some special liquids like carbon tetrachloride, toluene, xylene, decaline, and trichloroethylene can do the job. When this hot solution cools down, the polyethylene slowly comes out of the liquid.
Now, the interesting part is that it has these little branches in its molecule structure. These branches form while the plastic is being made, either by mixing different polythene molecules or by rearranging parts within a single molecule. This branching makes it different from high-density polyethylene, which is more like a long chain without branches.
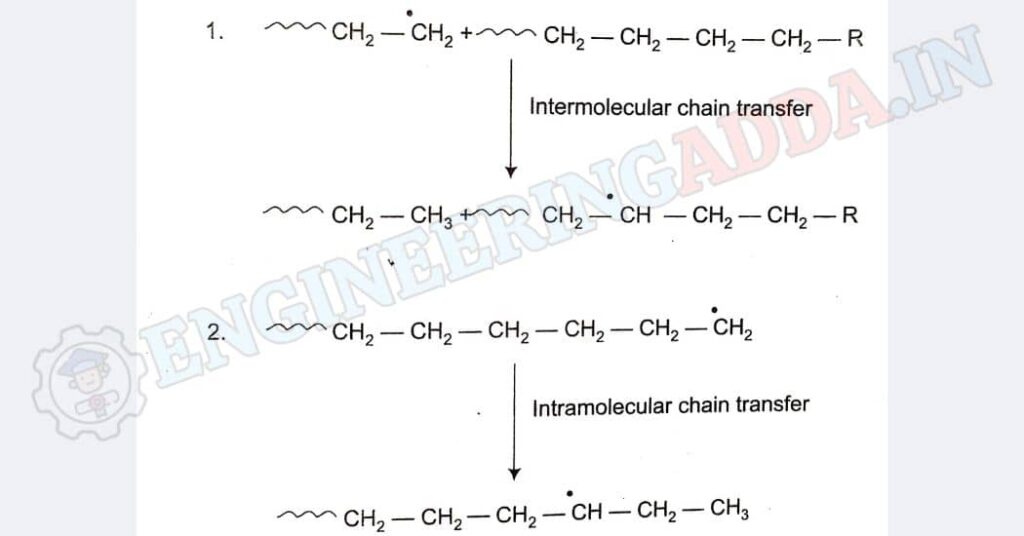
In the first case, the branches could be as long as the backbone chain itself, whereas, in the second case, the branches are much shorter in length.
High-density polyethylene
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is produced using two primary methods. The first method involves a process known as coordination polymerization. In this method, they use compounds like triethyl chromium and titanium tetrachloride to help the molecules of HDPE come together and form the plastic. The second method utilizes metal oxide catalysts, such as chromium or molybdenum oxides, which are supported on alumina-silica bases. These catalysts play a crucial role in initiating polymerization. What’s noteworthy is that both of these processes work well under relatively low pressure, making them efficient and cost-effective.
When we look at the properties of HDPE, it differs significantly from its counterpart, low-density polyethylene (LDPE). HDPE is exceptionally structured, with about 90% of its composition in a crystalline state. This characteristic results in a high density for the material, reaching up to 0.965 grams per cubic centimeter. Additionally, it exhibits a distinct melting point range, typically between 144 and 150 degrees Celsius.
Comparison
Compared to LDPE, HDPE is substantially more robust, harder, and stiffer. It can withstand higher levels of tension, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring strength and rigidity. Furthermore, it is more chemically resistant, which means it can endure exposure to various chemicals without deteriorating.
The primary uses of LDPE films are in the packaging and wrapping of textiles, frozen food, and other items. The film is remarkable in that it combines resistance to chemicals and moisture, high tear strength, low density, and exceptional flexibility. Without using a plasticizer, the polymer’s intrinsic attribute is the thin film’s flexibility. ‘Squeeze bottles’ and other eye-catching containers use LDPE because of their chemical inertness and shatterproof nature. Agricultural, irrigation, and domestic water line connections are all built with LDPE pipes. The polymer’s non-polar properties make it perfect for insulating electrical cables.
Toys and other household items are manufactured using HDPE. When extreme rigidity and tensile strength are needed, high-density polyethylene finds better use.
Another Website: Botorzo
Faq
What is polythene, and why is it popular?
Polythene, or polyethylene, is a popular plastic known for its flexibility, durability, and affordability.
What are the different types of polyethylene?
Polyethylene has variations like LDPE, HDPE, and LLDPE, each with unique characteristics and uses.
What are the environmental concerns?
Polyethylene’s non-biodegradability raises environmental worries, leading to recycling efforts.
How was polythene first created?
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) made polythene in 1933 by polymerizing ethylene.